Enthalpy
For any system, that is, the volume of substance under discussion, enthalpy is the sum of the internal energy of the system plus the system's volume multiplied by the pressure exerted by the system on its surroundings. The sum is given the special symbol H primarily as a matter of convenience because this sum appears repeatedly in thermodynamic discussion. Previously, enthalpy was referred to as total heat or heat content, but these terms are misleading and should be avoided. Enthalpy is, from the viewpoint of mathematics, a point function, as contrasted with heat and work, which are path functions. Point functions depend only on the initial and final states of the system undergoing a change; they are independent of the paths or character of the change. For change in enthalpy with pressure or temperature See Thermodynamic principles, Entropy, Thermodynamic processes
Enthalpy
enthalpy
[en′thal·pē]Enthalpy
the thermodynamic potential that characterizes the state of a thermodynamic system upon the selection of entropy 5 and pressure p as the principal independent variables (seePOTENTIALS, THERMODYNAMIC and ). Enthalpy is represented as H(S, p, N, xi), where N is the number of particles in the system and xi is the system’s other macroscopic parameter. It is an additive function; that is, the enthalpy of the entire system is equal to the sum of the enthalpies of its component parts. Enthalpy is related to the internal energy U of the system by the equation
(1) H = U + pV
where V is the volume of the system. The total enthalpy differential, given fixed N and xi, has the form
(2) dH = TdS + vdp
From formula (2) it is possible to determine the temperature T and the volume of the system: T = (αH/αS)p and V = (αH/αp)s. At constant pressure (p = const), the heat capacity of the system cp = (αH/αT)p (seeHEAT CAPACITY). These properties of enthalpy, at p = const, are similar to the properties of internal energy at constant volume:
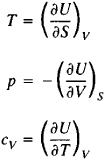
A minimum enthalpy value corresponds to the equilibrium state of a system given the constancy of S and p. A change in enthalpy (ΔH) is equal to the amount of heat imparted to the system or removed from it at constant pressure, therefore the values of ΔH characterize the heat effects of phase transitions (melting, boiling), chemical reactions, and other processes that occur at constant pressure. Enthalpy is conserved upon the thermal insulation of bodies (at p = const), and therefore it is sometimes called heat content or total heat. The condition for enthalpy conservation underlies, in particular, the theory of the Joule-Thomson effect, which has found important practical applications in the liquation of gases. The term “enthalpy” was proposed by H. KamerlinghOnnes.
D. N. ZUBAREV