elbow
1. the joint between the upper arm and the forearm, formed by the junction of the radius and ulna with the humerus
2. the corresponding joint or bone of birds or mammals
Collins Discovery Encyclopedia, 1st edition © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
Elbow
Sharp corner in a pipe or conduit, as opposed to a bend, which has a larger radius of curvature.
Illustrated Dictionary of Architecture Copyright © 2012, 2002, 1998 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
elbow
[′el‚bō] (anatomy)
The arm joint formed at the junction of the humerus, radius, and ulna.
(design engineering)
A fitting that connects two pipes at an angle, often of 90°.
A sharp corner in a pipe.
(electromagnetism)
In a waveguide, a bend of comparatively short radius, normally 90°, and sometimes for acute angles down to 15°.
(geography)
A sharp change in direction of a coast line, channel, bank, or so on.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright © 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
elbow
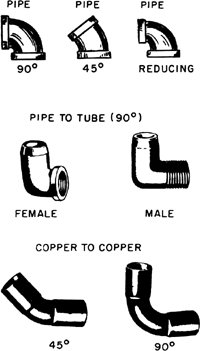
elbows, 1
1. A pipe, sheet metal, or conduit fitting having a bend, usually 90°; a 90° elbow is also called an ell.
2. A crossette, 1.
3. A shoulder, 1.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture and Construction. Copyright © 2003 by McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Elbow
ignorant, blundering constable. [Br. Lit.: Measure for Measure]
See: Stupidity
Allusions—Cultural, Literary, Biblical, and Historical: A Thematic Dictionary. Copyright 2008 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.