lignin
[′lig·nən]lignin
Lignin
a complex polymeric compound contained in the cells of vascular plants. It is one of the lining substances of the sheath of plant cells. The deposition of lignin in the cell membranes produces lignification of the cells and increases their strength. The wood of deciduous trees contains 20–30 percent lignin; that of coniferous varieties, up to 50 percent. Lignin has not been found in lower plants (algae and fungi or mosses). The ultrastructure of lignified cell membranes may be compared to the structure of reinforced concrete: the microfibrils of cellulose correspond in their properties to the reinforcement rods, and the lignin, which has high compressive strength, corresponds to the concrete. The chemical composition of lignin has not been conclusively established. The lignin molecule consists of the products of polymerization of aromatic alcohols, and the basic monomer is coniferyl alcohol:
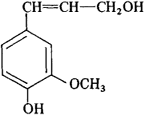
Lignin is an amorphous substance, yellowish brown in color; it is insoluble in water and organic solvents. It is stained by basic dyes and yields color reactions characteristic of phenols. The biosynthesis of lignin has not been completely studied. Its precursor is shikimic acid, which is also the case for a number of other aromatic compounds in plants. The formation of lignin takes place through the following basic stages: shikimic acid phenylalanine → cinnamic acid → ferulic acid → coniferyl alcohol → lignin.
REFERENCES
Kretovich, V. L. Osnovy biokhimii rastenii, 5th ed. Moscow, 1971.Frey-Wyssling, A., and K. Mühlethaler. Ul’trastruktura rastitel’noi kletki. Moscow, 1968. (Translated from English.)
Biokhimiia fenol’nykh soedinenii. Edited by J. Harborne. Moscow, 1968. (Translated from English.)
REFERENCES
Nikitin, N. I. Khimiia drevesiny i tselliulozy. Moscow-Leningrad, 1962.Brauns, F. E., and D. A. Brauns. Khimiia lignina. Moscow, 1964. (Translated from English.)
Khimiia drevesiny. Edited by B. L. Browning. Moscow, 1967. (Translated from English.)