rainbow
What does it mean when you dream about a rainbow?
The rainbow is a very happy and promising sign. Hopes and dreams are denoted by this wonderful symbol. Good luck comes to those who dream rainbow dreams.
rainbow
[′rān‚bō]rainbow
Rainbow
(1) See Rainbow Series.(2) Digital Equipment's original offering in the PC market. The Rainbow, released between 1982 and 1986, used an Intel 8088 to run MS/DOS, but could also run CP/M programs because its Z80 keyboard processor served as an alternate CPU. The Rainbow was not hardware-compatible with the IBM PC.
Rainbow
(dreams)Rainbow
an optical phenomenon of the atmosphere that resembles a multicolored are in the sky. A rainbow is observed when solar rays shine on water droplets that are in the part of the sky opposite the sun. The center of the are of a rainbow is located on a straight line that passes from the solar disk to the observer’s eye; that is, the center is at a point opposite the sun. The are of a rainbow is the part of a circle circumscribed around this point with a radius of 42° (see Figure 1).
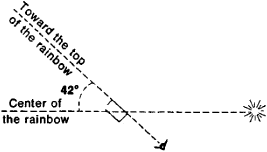
The color sequence in a rainbow is the same as in the solar spectrum. Red is usually located on the outside edge of the bow, and violet is usually on the inside edge. Secondary rainbows, which border on the main arc, are sometimes visible from the inside edge. The visible part of the rainbow are is determined by the sun’s position; when the sun is on the horizon, a rainbow is a semicircular are; as the sun rises, the visible part of the are decreases; and when the sun is at an altitude of 42°, the rainbow disappears.
A phenomenon similar to the rainbow may be observed in the spray of fountains and waterfalls. Moonbows and rainbows created by artificial light sources also occur. A secondary rainbow is frequently observed that has an angular radius of about 52° and a reversed color sequence.
The first rainbow theory was proposed in 1637 by R. Descartes. A more exact theory was developed in 1836 by the British astronomer G. Airy and in the late 19th century by the Austrian geophysicist I. M. Pernter. This theory is based on calculating the diffraction and interference effects that accompany the encounter of solar rays with the curtain formed by raindrops.