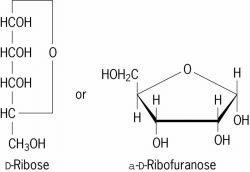
Ribose
A water-soluble pentose, also known as d -ribose (see first structural formula), which, together with 2-deoxy- d -ribose, makes up the carbohydrate constituents of nucleic acids, which are found in all living organisms. The universal occurrence of nucleic acids in all living cells makes this pentose highly interesting to biochemists and biologists. The type of nucleic acid that yields d -ribose is referred to as ribonucleic acid (RNA). d -Ribose is a constituent not only of the nucleic acids, but also of several vitamins and coenzymes. As in the nucleic acids, this sugar occurs in the furanose
configuration (see second structural formula) in these natural products. See Coenzyme, Deoxyribose, Nucleic acid, Vitaminribose
[′rī‚bōs]Ribose
a monosaccharide belonging to a group of pentoses (aldopentoses). Ribose exists as optically active D-ribose and L-ribose and as an inactive racemate. Ribose crystals are readily soluble in water. The melting point for D-ribose is 86°–87°C. Ribose characteristically has a high (8.5 percent) acyclic (aldehyde) content in solution. D-ribose is found in all living organisms. It is a component of the most important compounds that effect the transfer of information and energy in cells; these compounds include ribonucleic acids, nucleosides, mononucleotides and dinucleotides. Some coenzymes and bacterial polysaccharides also contain D-ribose.