Solar Photochemical Unit
an apparatus that makes use of solar radiation to achieve photochemical reactions. As of 1975, such units were for the most part still in the experimental stage. A solar photochemical unit usually consists of an optical system (including a concentrator and an orientating device), a photochemical reactor in the form of a glass vessel, and an automatic control system.
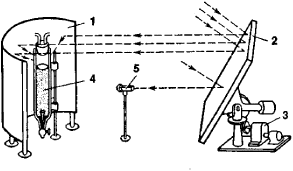
A promising use of solar photochemical units is for the nitrosation of cyclohexane in the production of caprolactam (see Figure 1). It is advisable to operate such a unit in combination with two other units: a cooling unit to maintain a constant reactor temperature and a chemical unit to process the substances needed for the nitrosation reaction. All three units can be operated on solar energy and thus can form a single system.