Solubility Diagram
a graphic representation of the equilibrium composition of solutions as a function of temperature, pressure, or other parameter characterizing the external conditions.
The solubility diagram is a special type of phase diagram, the latter being widely used in chemical thermodynamics. A solubility diagram for a system made up of two partially miscible liquid components A and B, nitrobenzene and n-hexane, is shown in Figure 1. Each point a’ outside the shaded region corresponds to an unsaturated solution of one component in the other; each point on the curve bounding this region represents a saturated solution; and each point inside the shaded region corresponds to a two-phase system from the layer of the saturated solution of A in B, whose composition is denoted by point b, and from the layer of the saturated solution of B in A, whose composition is denoted by point c.
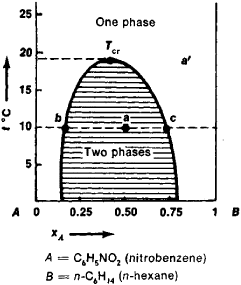
Complete miscibility occurs in many systems at temperatures above a certain TCT —the critical solution temperature. The compositions of both layers are identical at this temperature. If the curve bounding the two-phase region has a maximum, TCT is called the upper critical solution temperature (Figure 1); if it has a minimum, it is called the lower critical solution temperature. The solubility diagrams for certain systems, for example, water-nicotine, contain both critical temperatures.