spherical sector
[′sfir·ə·kəl ′sek·tər] (mathematics)
A solid formed by rotating a sector of a circle about a diameter of the circle; the diameter may contain one of the radii bounding the circular sector or it may lie outside the circular sector.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright © 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
The following article is from The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (1979). It might be outdated or ideologically biased.
Spherical Sector
(or sector of a sphere), the geometric solid generated by the rotation of a sector of a circle about one of the radii bounding the sector (Figure 1,a) or about a diameter that does not intersect the arc bounding the sector (Figure 1,b).
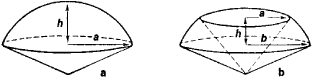
Figure 1
The volume of both types of spherical sector is V = 2πR2h/3. The area of the surface of the first type of spherical sector is S1 = πR(2h + a); the corresponding area for the second type of spherical sector is S2 = πR(2h + a + b). Here, R is the radius; h is the length of the projection, onto the axis of rotation, of the chord joining the endpoints of the arc; and a and b are the distances of the endpoints from the axis.
The Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition (1970-1979). © 2010 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.