bearing
1. a support, guide, or locating piece for a rotating or reciprocating mechanical part
2. the angular direction of a line, point, or course measured from true north or south (true bearing), magnetic north or south (magnetic bearing), or one's own position
3. the position or direction, as of a ship, fixed with reference to two or more known points
Collins Discovery Encyclopedia, 1st edition © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
bearing
[′ber·iŋ] (civil engineering)
That portion of a beam, truss, or other structural member which rests on the supports.
(mechanical engineering)
A machine part that supports another part which rotates, slides, or oscillates in or on it.
(mining engineering)
The direction of a mine drivage, usually given in terms of the horizontal angle turned off a datum direction, such as the true north and south line.
(navigation)
The horizontal direction from one terrestrial point to another; basically synonymous with azimuth.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright © 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
bearing
2. That portion of a beam, truss, or other structural member which rests on the supports.
3. The support for a shaft, axle, or trunnion.
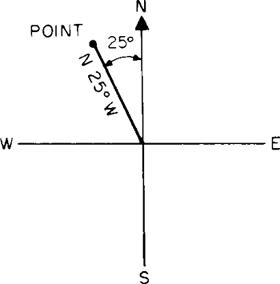
4. In surveying, the horizontal angle between a line and a reference meridian adjacent to the quadrant in which the line lies.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture and Construction. Copyright © 2003 by McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
bearing

Spherical roller thrust bearing.
. The horizontal angle at a given point measured clock-wise from a specific reference datum to a second point. The bearing can be true, magnetic, relative, or grid, depending on the selected datum.
ii. A surface that supports and reduces friction between two moving points.
An Illustrated Dictionary of Aviation Copyright © 2005 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
The following article is from The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (1979). It might be outdated or ideologically biased.
Bearing
in navigation, the angle between the meridian plane of the observer and the vertical plane passing through the point of observation and the observed object. The bearing angle is the same as the azimuth. Bearings are designated as true, magnetic, or compass bearings, depending on the type of meridian from which they are reckoned.
There are several systems for taking bearings. In the circular method, lines of position are stated in degrees clockwise from the northerly meridian. In the semicircular method, lines of position can be read clockwise in degrees from the northerly and southerly meridians. The quadrant method states lines of position in terms of quadrants; that is, the bearing angle is read with respect to the northerly and southerly meridian clockwise and counterclockwise between the limits of 0° and 90°. The rhumb method is also used, in which bearings are taken by dividing the circle of the compass into 32 rhumbs and reading from the northerly meridian.
Bearing
a shaft or axle support that fixes the position of a rotating or rocking part of a mechanism relative to the other parts. Bearings are classified according to the direction of loading as radial, taking loads perpendicular to the axis of the shaft; thrust, taking loads directed along the axis of the shaft; and radial-thrust, taking composite loads, mostly radial (thrust-radial bearings, taking mainly axial loads, are used less frequently). Bearings are also distinguished according to the type of friction as rolling-contact (the more common) and plain types.
The Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition (1970-1979). © 2010 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.