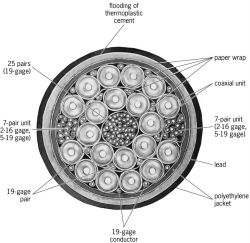
coaxial cable
[kō′ak·sē·əl ′kā·bəl]Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
An electrical transmission line comprising an inner, central conductor surrounded by a tubular outer conductor. The two conductors are separated by an electrically insulating medium which supports the inner conductor and keeps it concentric with the outer conductor. One version of coaxial cable has periodically spaced polyethylene disks supporting the inner conductor. This coaxial is a building block of multicoaxial cables used in L-carrier systems (see illustration).
The symmetry of the coaxial cable and the fact that the outer conductor surrounds the inner conductor make it a shielded structure. At high frequencies, signal currents concentrate near the inside surface of the outer conductor and the outer surface of the inner conductor. This is called skin effect. The depth to which currents penetrate decreases with increasing frequency. Decreased skin depth improves the cable's self-shielding and increases transmission loss. This loss (expressed in decibels per kilometer) increases approximately as the square root of frequency because of the skin effect.
Coaxial cables can carry high power without radiating significant electromagnetic energy. In other applications, coaxial cables carry very weak signals and are largely immune to interference from external electromagnetic fields.
A coaxial cable's self-shielding property is vital to successful use in broadband carrier systems, undersea cable systems, radio and TV antenna feeders, and community antenna television (CATV) applications.
Coaxial units are designed for different mechanical behavior depending upon the application. Widely used coaxials are classified as flexible or semirigid.
coaxial cable
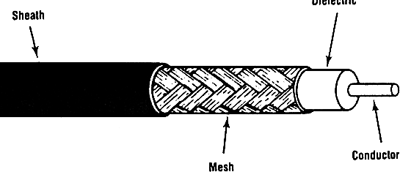
coaxial cable
(hardware)coaxial cable
A strong, flexible, high-capacity cable widely used in audio, video and data applications. Commonly called "coax" (pronounced "co-axe"), the cable comprises a solid or stranded wire in the center, surrounded by insulation. The insulation is wrapped with a metallic foil or braided wire that serves as the ground line and interference shield. All of this is enclosed in a plastic cover, which may have a fire-safe Teflon coating.There Are Many Types
Typically with impedances of 50 or 75 Ohms, cables have different outside diameters and maximum capacities for operating voltage. Designated with an RG (radio grade) prefix such as RG-6, cables are also rated for signal loss (attenuation in dBs per 100 feet). Following are common types; however, there are many more in use. See RCA connector and F connector.
Impedance Core Layers Range in Dia. inType Ohms (mm) Sheath RG-6 75-76 1.0 2 RG-6 Quad 75-76 1.0 4 RG-58 50-53.5 0.9 1 RG-59 73-75 0.81 1 RG-59 Quad 73-75 0.81 4
| Coaxial Cable |
|---|
| Coax uses two wires. The inner wire is the primary conductor. The ground wire is an aluminum or copper sheath that surrounds the insulation of the primary conductor and also serves as a shield against external interference. |
Coaxial Cable
a cable in which the wires that constitute the circuit are two coaxial cylinders. Coaxial cables are used for transmitting electric signals over telecommunications lines, as antenna feeders for radio, electronic and television apparatus, and as connections between units of radio apparatus.
The electromagnetic field of a coaxial cable is concentrated in the space between the conductors—that is, there is no external field, and thus there are virtually no radiation losses into the space surrounding the cable. The outer wire also functions as an electromagnetic screen, protecting the electric circuit from outside influences. Therefore, coaxial cables exhibit a high degree of noise immunity. Energy losses of transmitted signals are comparatively low.
Coaxial communications cables are characterized by the diameter of the inner and outer wires, which are usually given in the model number—for example, KPK-5/18 (coaxial submarine cable with an inner wire 5 mm in diameter and an outer wire 18 mm in diameter). Radio-frequency cables of coaxial design are marked differently; their model numbers reflect only the inside diameter of the outer wire.
D. L. SHARLE