photometer
Photometer
An instrument used for making measurements of light, or electromagnetic radiation, in the visible range. In general, photometers may be divided into two classifications: laboratory photometers, which are usually fixed in position and yield results of high accuracy; and portable photometers, which are used in the field or outside the laboratory and yield results of lower accuracy. Each class may be subdivided into visual (subjective) photometers and photoelectric (objective or physical) photometers. These in turn may be grouped according to function, such as photometers to measure luminous intensity (candelas or candlepower), luminous flux, illumination (illuminance), luminance (photometric brightness), light distribution, light reflectance and transmittance, color, spectral distribution, and visibility. Visual photometric methods have largely been supplanted commercially by physical methods, but because of their simplicity, visual methods are still used in educational laboratories to demonstrate photometric principles. See Illuminance, Luminance, Luminous flux, Luminous intensity
photometer
(foh-tom -ĕ-ter) An instrument used in photometry, such as a CCD, photovoltaic detector, photomultiplier, photodiode, or bolometer. In these devices the incident radiation is converted into an electrical signal whose magnitude can be determined very precisely.Photometer
photometer
[fō′täm·əd·ər]Photometer
An instrument used for making measurements of light, or electromagnetic radiation, in the visible range. In general, photometers may be divided into two classifications: laboratory photometers, which are usually fixed in position and yield results of high accuracy; and portable photometers, which are used in the field or outside the laboratory and yield results of lower accuracy. Each class may be subdivided into visual (subjective) photometers and photoelectric (objective or physical) photometers. These in turn may be grouped according to function, such as photometers to measure luminous intensity (candelas or candlepower), luminous flux, illumination (illuminance), luminance (photometric brightness), light distribution, light reflectance and transmittance, color, spectral distribution, and visibility. Visual photometric methods have largely been supplanted commercially by physical methods, but because of their simplicity, visual methods are still used in educational laboratories to demonstrate photometric principles.
photometer
Photometer
an instrument for the measurement of photometric quantities. When a photometer is operated, some spatial restriction is imposed on the radiation flux, which is registered by a radiation detector with a specific spectral sensitivity.
Illuminance is measured with luxmeters, luminance with luminance photometers, and luminous flux and luminous energy with integrating-sphere photometers. The instruments used for measuring the color of an object are called colorimeters. If the eye is used as a detector, the photometer is known as a visual photometer; if a physical detector is used, it is called a physical photometer. The optical assembly of a photometer, sometimes called the photometric head, contains lenses, light-diffusing plates, light attenuators, light filters, diaphragms, and a radiation detector. In photometers with physical detectors, the radiation flux is usually converted into an electrical signal, which is registered by means of a microammeter, voltmeter, or other type of instrument. In flicker photometers, the indicating instruments used are electrometers, storage oscillographs, and peak voltmeters. In a visual photometer the brightnesses of two fields separately illuminated by the luminous fluxes to be compared are equalized by eye through an eyepiece on the photometric head.
The optical designs of photometers (Figure 1) used to determine dimensional photometric quantities provide either a constant geometric factor or a change in the factor according to some specific relationship. The systematic measurement errors of photometers having an absolute calibration are typically large (it is difficult to reduce the error to less than 5 percent). Qualified specialists
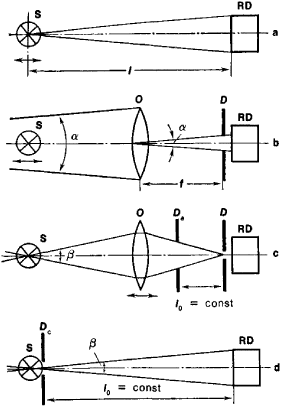
in well-equipped laboratories are usually able to make measurements with errors of 10–20 percent. Errors in the measurement installation itself may increase the error to 50 percent or more.
The accuracy of photometers used to measure the ratio of radiation fluxes (transmission factors and reflection coefficients) is very high. Such instruments may be constructed with one or two optical channels. Single-channel photometers measure the relative reduction in the radiation flux when a specimen is placed in the path of the rays. In a two-channel photometer the radiation flux is attenuated by the specimen as fluxes in the measuring and reference channels are compared. The fluxes are made equal by means of adjustable diaphragms, photometer wedges, or similar devices. The transmission factors and reflection coefficients of light-diffusing specimens may also be measured by integrating-sphere photometers.
A. S. DOINIKOV