Pyrimidine
A heterocyclic organic

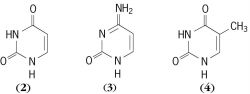
Pyrimidine compounds which are found universally in living organisms include uracil ( 2 ), cytosine ( 3 ), and thymine
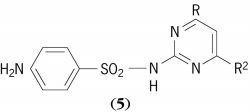
( 4 ). Together with purines these substances make up the “bases” of nucleic acids, uracil and cytosine being found characteristically in ribonucleic acids, with thymine replacing uracil in deoxyribonucleic acids. A number of related pyrimidines also occur in lesser amounts in certain nucleic acids. Other pyrimidines of general natural occurrence are orotic acid and thiamine (vitamin B1). See Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), Purine, Ribonucleic acid (RNA)Among the sulfa drugs, the pyrimidine derivatives, sulfadi-azine, sulfamerazine, and sulfamethazine, have general formula ( 5 ).
These agents are inhibitors of folic acid biosynthesis in microorganisms. The barbiturates are pyrimidine derivatives which possess potent depressant action on the central nervous system.pyrimidine
[pə′rim·ə‚dēn]Pyrimidine
(also called 1,3-diazine), a heterocyclic compound. Colorless crystals; melting point, 21°C; boiling point, 124°C. Pyrimidine is readily soluble in water, alcohol, and ether. The structural formula is

Pyrimidine is a very weak, monoacidic base that forms quaternary salts, each of which contains a single nitrogen atom; it also reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to yield N-oxides. Pyrimidine does not enter readily into electrophilic substitution reactions, for example, halogenation, sulfonation, and nitration, but the hydrogen atom on the carbon in position number four is easily replaced in reactions with organomagnesium compounds, organolithium compounds, NaNH2, and KOH. Pyrimidine is synthesized by reduction of its 2,4,6-trichloro derivative, which is a product of the reaction of POCI3 with barbituric acid. Pyrimidine and its derivatives are components of individual nucleotides and of nucleic acids, the most important biopolymers. They also occur in many biologically active substances, including thiamine, the antibiotic, amicetin, and barbiturates.