radiator
1. a device for heating a room, building, etc., consisting of a series of pipes through which hot water or steam passes
2. a device for cooling an internal-combustion engine, consisting of thin-walled tubes through which water passes. Heat is transferred from the water through the walls of the tubes to the airstream, which is created either by the motion of the vehicle or by a fan
3. Electronics the part of an aerial or transmission line that radiates electromagnetic waves
4. an electric space heater
Collins Discovery Encyclopedia, 1st edition © HarperCollins Publishers 2005
Radiator
A heating unit which transfers heat by radiation; usually fed by hot water or steam.
Illustrated Dictionary of Architecture Copyright © 2012, 2002, 1998 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
radiator
[′rād·ē‚ād·ər] (acoustics)
A vibrating element of a transducer which radiates sound waves.
(electromagnetism)
The part of an antenna or transmission line that radiates electromagnetic waves either directly into space or against a reflector for focusing or directing.
A body that emits radiant energy.
(engineering)
Any of numerous devices, units, or surfaces that emit heat, mainly by radiation, to objects in the space in which they are installed.
(physics)
In general, a body which emits particles or radiation in any form.
A body placed in a beam of ionizing radiation which, as a result, emits radiation of another kind.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright © 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Radiator
Any of numerous devices, units, or surfaces that emit heat, mainly by radiation, to objects in the space in which they are installed. Because their heating is usually radiant, radiators are of necessity exposed to view. They often also heat by conduction to the adjacent thermally circulated air.
Radiators are usually classified as cast-iron (or steel) or nonferrous. They may be directly fired by wood, coal, charcoal, oil, or gas (such as stoves, ranges, and unit space heaters). The heating medium may be steam, derived from a steam boiler, or hot water, derived from a water heater, circulated through the heat-emitting units.
Electric heating elements may be substituted for fluid heating elements in all types of radiators, convectors, and unit ventilators. See Hot-water heating system, Radiant heating, Steam heating
McGraw-Hill Concise Encyclopedia of Engineering. © 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
radiator

radiator
A heating unit usually exposed to view within the room or space to be heated; transfers heat by radiation to objects within visible range, and by conduction to the surrounding air, which in turn is circulated by natural convection; usually fed by steam or hot water.
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture and Construction. Copyright © 2003 by McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
radiator
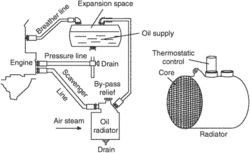

Radiator.
. The source of radiant energy. It could be a source of electromagnetic radiation such as a hostile radar or a radio transmitter.
ii. A heat exchanger, which dumps undesired heat into the atmosphere.
An Illustrated Dictionary of Aviation Copyright © 2005 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
The following article is from The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (1979). It might be outdated or ideologically biased.
Radiator
one of the most common heating devices used in heating systems for residential, public, and industrial buildings.
The radiators most commonly used in the USSR are made of cast iron and consist of interconnected two-channel core sections through which the heat-transfer agent (water or steam) circulates; the number of sections depends on the rated heating surface. Other types of cast-iron radiators used include single-channel radiators in the USSR and, in other countries, multichannel radiators, with up to nine channels in each section. Single or paired stamped steel radiators of the panel type, also called heating panels, are becoming popular; considerably less metal is consumed in their manufacture. Porcelain and ceramic radiators, which meet very high sanitary and health requirements, are sometimes used.
Radiator
a device for removing heat from the liquid that circulates through the cooling system of an internal-combustion engine. A radiator consists of a core (the cooling part), with upper and lower headers (reservoirs) and connecting pipes. Radiator cores may have several staggered rows of oval brass tubes, with cooling fins soldered to the tubes, or one row of flat brass tubes with fins soldered to them. The upper header has a filler neck with a leakproof cap containing a combined pressure and vacuum relief valve. There is a valve in the lower header for draining the coolant.
The Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 3rd Edition (1970-1979). © 2010 The Gale Group, Inc. All rights reserved.

