theodolite
[thē′äd·əl‚īt]theodolite

theodolite

Theodolite
(or transit), a geodetic instrument for determining directions and measuring horizontal and vertical angles during geodetic work and topographic and mine surveying, in construction, and in other applications. Horizontal and vertical circles calibrated in degrees and smaller units are the main measuring devices in the theodolite.
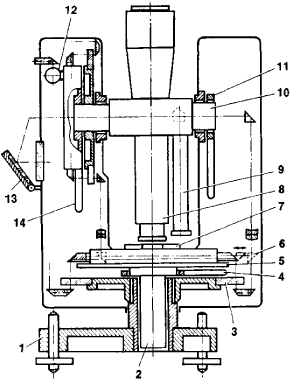
Until the mid-20th century, theodolites with metal circles read by means of verniers or micrometric microscopes were used. In the 1920’s, theodolites with glass circles equipped with optical reading devices appeared, and they came to be called optical theodolites. Schematic and optical diagrams of a theodolite are given in Figures 1 and 2, respectively; the devices for the vertical circle analogous to those for the horizontal circle are not shown.
In the USSR, GOST (the All-Union State Standard) permits only the manufacture of optical theodolites, whose main specifications are given in Table 1 (the number included in the type name is the permissible mean square error of measurement of the horizontal angle in seconds of arc).
Theodolites often have various attachments, such as a declinometer, sighting marks, or an optical range finder.
| Table 1. Specifications of main Soviet theodolites | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter of circles (mm) | Scale divisions | Magnification of telescope | Maximum measurement of Vertical angles | Weight in case (kg) | |||
| vertical | Horizontal | Circles | Reading device | ||||
| Note: The reading devices of the T05, T1, and T2 are optical micrometers, that of the T5 and T15 are scale microscopes, and that of the T30 is an index | |||||||
| T05 ............... | 180 | 130 | 10’ | 1” | 35 × | 50° | 21 + 15 |
| 50 × | two | ||||||
| 60 × | pieces | ||||||
| T1 ............... | 135 | 90 | 10’ | 1” | 30 × | 65° | 13.5 |
| 40 × | |||||||
| T2 ............... | 90 | 65 | 20’ | 1” | 25 × | 75° | 95 |
| T5 ............... | 95 | 70 | 1° | 1° | 28 × | 65° | 6 5 |
| T15 ............... | 72 | 72 | 1° | 2’ | 25 × | 60° | 40 |
| T30 ............... | 72 | 72 | 10’ | – | 20 × | 55° | 3.2 |
Various kinds of specialized theodolites exist. Among them are astronomical theodolites, which allow sighting on the zenith and have ocular micrometers; tachymeters, which automatically give the difference in elevation of points according to readings on a scale; mine surveying theodolites, for work in mine shafts; gyroscopic theodolites, for determining the direction of the meridian; and theodolites that automatically record the results on punched tape for feeding to a computer.

The theodolite has a number of typical instrument errors, whose effect is diminished by well-thought-out design, careful manufacture and testing, and appropriate measurement techniques.
REFERENCES
GOST 10529-70: Teodolity. Tipy. Osnovnye parametry i teknicheskie trebovaniia.GOST 20063-74: Teodolity. Metody ispytanii i proverki.
Eliseev, S. V. Geodezicheskie instrumenty ipribory, 3rd ed. Moscow, 1973.
Deimlich, F. Geodezicheskoe instrumentovedenie. Moscow, 1970. (Translated from German.)
Zakharov, A. I. Novye teodolity i opticheskie dal’nomery. Moscow, 1970.
G. G. GORDON