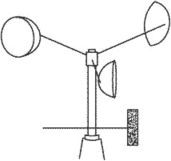
anemometer
Anemometer
An instrument to measure the speed or velocity of gases either in a contained flow, such as airflow in a duct, or in unconfined flows, such as atmospheric wind. To determine the velocity, an anemometer detects change in some physical property of the fluid or the effect of the fluid on a mechanical device inserted into the flow.
An anemometer can measure the total velocity magnitude, the velocity magnitude in a plane, or the velocity component in a particular direction. The cup anemometer, for example, measures the velocity in a plane perpendicular to the axis of its rotation cups. If the cup anemometer is mounted with the shaft perpendicular to the horizontal, it will measure only the component of the wind that is parallel to the ground. Other anemometers, such as the pitot-static tube, are used with the tip aligned with the total velocity vector. Before using an anemometer, it is important to determine how it should be positioned and what component of the total velocity its measurement represents.
An anemometer usually measures gas flows that are turbulent. The cup anemo meter, pitot-static tube, and thermal anemometer are mostly used to measure the mean velocity, while the hot-wire, laser Doppler, and sonic anemometers are usually used when turbulence characteristics are being measured. (The term “thermal anemometer” is often used to mean any anemometer that uses a relationship between heat transfer and velocity to determine velocity.)
anemometer
[‚an·ə′mäm·əd·ər]anemometer
anemometer