streptomycin
streptomycin
[‚strep·tə′mīs·ən]Streptomycin
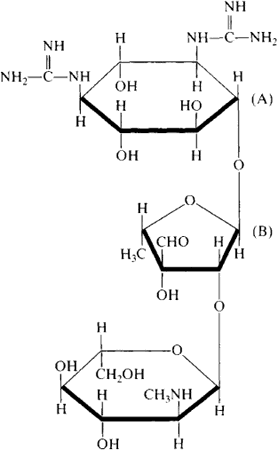
an antibiotic produced by fungi of the genus Actinomyces (Streptomyces). Streptomycin was first obtained in 1944 from A. griseus by the American scientist S. A. Waksman and his colleagues. Chemically, streptomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic; in acid hydrolysis, the molecule breaks down into streptidine (A; see formula) and streptobiosamine (B). Chemically, streptidine is the hexatomic cyclic alcohol inositol substituted by two guanidine groups. Streptobiosamine is a disaccharide containing a methylamino group. Streptomycin has the properties of a base; it dissolves readily in water and is virtually insoluble in organic solvents. It easily forms salts with various acids. The molecular weight is 581.6. In a dried state, streptomycin remains active for more than two years.
A broad-spectrum antibiotic, streptomycin is active against tuberculosis bacteria and the pathogens of plague, tularemia, brucellosis, and dysentery. It is also active against Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci, gonococci, and menin-gococci but is not active against fungi, protozoans, anaerobic microbes, spirochetes, rickettsiae, or viruses. Attaching itself to ribosomes in the bacterial cell, streptomycin interferes with the reading of the genetic code and inhibits the biosynthesis of protein. The primary mechanism of streptomycin’s effect has not been definitely established. Since with the clinical use of streptomycin strains of resistant bacteria are formed, the antibiotic is used in combination with other compounds. Streptomycin is most effective in the treatment of tuberculosis; it is also used in treating meningitis, endocarditis, whooping cough, gonorrhea, and many other diseases. The most serious side effects arising from prolonged use of streptomycin are vestibular disorders and impairment of hearing.
In the USSR, streptomycin is used in various forms, among which are streptomycin sulfate, a calcium chloride complex of streptomycin, the streptomycin salt of saluside (streptosaluside), and certain combinations (streptocillin, streptodimycin). Dihy-drostreptomycin, a product of the partial reduction of streptomycin, is also used. Streptomycin is used in biochemistry in studying the functions of ribosomes and the mechanism of protein biosynthesis.
REFERENCES
Khimiia antibiotikov, 3rd ed., vol. 1. Moscow, 1961.Kan, G. S. Streptomitsin. Moscow-Leningrad, 1962.
Navashin, S. M., and I. P. Fomina. Spravochnikpo antibiolikam, 3rd ed. Moscow, 1974.
Molekuliarnye osnovy deistviia antibiotikov. Moscow, 1975. (Translated from English.)
Streptomycin: Nature and Practical Applications. Edited by S. A. Waksman. Baltimore, Md., 1949.
L. E. GOL’DBERG