fold
1fold
2fold
[fōld]fold
(1) For foldable phones, see Galaxy Fold and iPhone Fold.(2) An invisible line on a Web page that is at the bottom of the first full page on screen. The fold determines how much is visible at first glance (see above the fold).
Fold
(also flexure), a tectonic structure in which a stratum or bed is strongly bent in two opposite directions. A fold consists of five elements, namely, two bends and three limbs. Two of the limbs are outside the bends; the third, or middle, limb connects the bends. Each element is described by its own bedding parameters, and the relationships between the parameters determine the many varieties of folds.
According to the bedding of the limbs, we distinguish among simple, plunging, and cross folds; according to the inclination of the hinges of the bends, folds are classified as vertical, inclined, and nonplunging (Figure 1). The size of a fold ranges from fractions of a meter to many kilometers. The inclination of the limbs ranges from barely discernible to vertical.
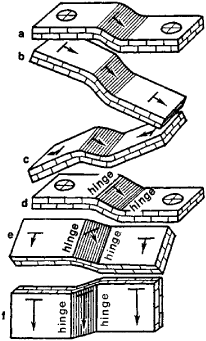
Note on Figure 1. Location of the strata in the major types of folds:, (a) simple fold, (b) plunging fold, (c) cross fold, (d) nonplunging fold, (e) inclined fold, (f) vertical fold; the symbol ![]() indicates that the strata are horizontal, the symbol
indicates that the strata are horizontal, the symbol ![]() shows the direction in which the strata dip
shows the direction in which the strata dip
Folds are found in cratons and folded regions. Especially large folds are found along the margins of cratons and the edges of syneclises. Some folds affect the accumulation of sediment and determine the distribution of the facies and thicknesses of sedimentary strata. Folds are sometimes associated with petroleum deposits.