Colorado
Colorado State Information
www.colorado.gov
Area (sq mi):: 104093.57 (land 103717.53; water 376.04) Population per square mile: 45.00
Population 2005: 4,665,177 State rank: 0 Population change: 2000-20005 8.50%; 1990-2000 30.60% Population 2000: 4,301,261 (White 74.50%; Black or African American 3.80%; Hispanic or Latino 17.10%; Asian 2.20%; Other 11.10%). Foreign born: 8.60%. Median age: 34.30
Income 2000: per capita $24,049; median household $47,203; Population below poverty level: 9.30% Personal per capita income (2000-2003): $33,370-$34,561
Unemployment (2004): 5.60% Unemployment change (from 2000): 2.90% Median travel time to work: 24.30 minutes Working outside county of residence: 33.00%
List of Colorado counties:
Colorado Parks
- US National Parks
- Urban Parks
- State Parks
- Parks and Conservation-Related Organizations - US
- National Wildlife Refuges
- National Trails
- National Scenic Byways
- National Heritage Areas
- National Grasslands
- National Forests
Colorado
Thirty-eighth state; admitted on August 1, 1876
State capital: Denver
Nickname: Centennial State
State motto: Nil sine Numine (Latin “Nothing without the Diety”)
State animal: Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis)
State bird: Lark bunting (Calamospiza melanocoryus Stejneger)
State fish: Greenback cutthroat trout (Oncorhynchus clarki somias)
State flower: Columbine (Aguilegia caerules)
State folk dance: Square dance
State fossil: Stegosaurus
State gem: Aquamarine
State grass: Blue Grama
State insect: Colorado Hairstreak Butterfly (Hypaurotis cysalus)
State mineral: Rhodochrosite
State rock: Yule marble
State song: “Where the Columbines Grow” and “Rocky Mountain High”
State tartan: Colorado State Tartan
State tree: Colorado blue spruce (Picea pungens)
More about state symbols at:
www.colorado.gov/dpa/doit/archives/history/symbemb. htm
SOURCES:
AmerBkDays-2000, p. 555 AnnivHol-2000, p. 128 DictDays-1988, p. 22
STATE OFFICES:
State web site: www.colorado.gov
Office of the Governor 136 State Capitol Bldg Denver, CO 80203 303-866-2471
fax: 303-866-2003
www.colorado.gov/governor
Secretary of State
1700 Broadway
2nd Fl
Denver, CO 80290
303-894-2200
fax: 303-894-4860
www.sos.state.co.us
Colorado State Library
201 E Colfax Ave
Rm 309
Denver, CO 80203
303-866-6900
fax: 303-866-6940
www.cde.state.co.us/index_library.htm
Colorado
a state in the western USA. Area, 270,000 sq km. Population, 2.2 million (1970); urban population, 78.5 percent. Capital and largest city, Denver.
The state’s territory is crossed in its central part from north to south by the Rocky Mountains (Mount Elbert, 4,399 m). Located in the east are the Great Plains and in the west, the Colorado Plateau. The climate is moderate and continental. The average January temperature in the plains and the plateau ranges from 0° to 4°C and in July, from 20° to 22°C. Annual precipitation amounts to 300–400 mm. The principal rivers are the South Platte, Arkansas, Rio Grande, and Colorado. Vegetation in the east is of the steppe type, and in the west it is semidesert. The mountain slopes are covered, for the most part, by coniferous forests.
Colorado is an industrial-agrarian state. In 1969 the mining industry included 13,000 employees and the processing industry, 114,000. Ores of rare and nonferrous metals are mined, as well as uranium, gold, petroleum, and coal; Colorado is in first place in the USA in the mining of molybdenum (the deposit at Climax). There is a food-processing industry (meat canning, sugar, and flour); ferrous (Pueblo) and nonferrous metallurgy are developed, as well as the metalworking, chemical, and rubber industries. The state has diverse machine-building industries (the production of mining and road-building equipment, radio elecironies, and space rockets); the chief center is Denver (with more than three-fourths of the employees in Colorado’s processing industry).
The foremost branch of agriculture is livestock raising for meat (for the most part, younger animals); in 1970 the state had 3.3 million head of cattle, including 100,000 milch cows; 300,000 pigs; and 1.2 million sheep. Sown on the irrigated lands in the river valleys are sugar beets, potatoes, and fodder grasses (especially various types of alfalfa). On the Great Plains the principal crop is wheat. Large commercial farms predominate.
V. M. GOKHMAN
Colorado
a river primarily in the USA, with its lower course in Mexico. Length, 2,740 km (with its right tributary, Green River, 3,200 km); basin area, 635,000 sq km.
The river rises in the forerange of the Rocky Mountains and flows into the Gulf of California in the Pacific Ocean, forming a delta with an area of 8,600 sq km. It flows primarily through the semidesert and desert regions of Utah and Arizona. It cuts through the Colorado Plateau and forms deep canyons with a total length of approximately 800 km, including one of the largest in the world—the Grand Canyon. The major left tributaries are the San Juan, Little Colorado, and Gila. The river is fed by snows from the Rocky Mountains. High flows of water begin in April and end in July; during the autumn and winter low flows occur.
The average discharge of water at Lees Ferry (the middle course) is 508 cu m per sec; at its mouth the discharge is only 5 cu m per sec as a result of the almost complete diversion of water by canals and aqueducts for irrigation and for supplying the cities on the California coast of the USA (including Los Angeles) with water. For this purpose the Glen Canyon Dam was built (at a point below the juncture of the San Juan) as well as the Hoover Dam (Boulder Dam), which form, respectively, the major reservoirs of Lake Powell and Lake Mead (each with an area of about 650 sq km and a volume of more than 34 cu km); also among those constructed are the Davis and Parker dams with the smaller Mojave and Havasu reservoirs (all these dams have hydroelectric power plants), as well as the Palo Verde, Imperial, and Morelos water-diversion canals. There are large reservoirs and irrigation systems in the Gila River basin (the Roosevelt, Santa Clara, Horseshoe and other reservoirs). The Colorado carries along a great deal of sediment (an average of 160 million tons annually), which is almost all deposited in the Powell and Mead reservoirs. In its lower reaches the Colorado is navigable for riverboats, but for transportation it is insignificant.
REFERENCES
Freeman, L. R. The Colorado River. London, 1923.Powell, J. W. Exploration of the Colorado River. New York, 1961.
O. A. SPENGLER
Colorado
a river in the southern part of the USA, located in the state of Texas. Length, 1,450 km; basin area, 107,000 sq km.
The river rises in the plateau of the Llano Estacado, and it flows into the Gulf of Mexico. In the spring there are floods and in the summer, freshets. The average discharge of water is 81 cu m per sec. There are many reservoirs, which are used for irrigation. The city of Austin is situated on the Colorado River.
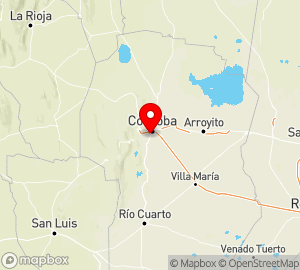
Colorado
a river in Argentina, in northern Patagonia. The Colorado measures more than 1,200 km long and drains an area of approximately 350,000 sq km. Formed by the confluence of the Grande and Barrancas rivers, which originate on the eastern slopes of the Andes, it crosses the dry region of northern Patagonia in a deep, wide valley and empties into Bahía Blanca of the Atlantic Ocean, forming a delta. There are flash floods, mainly in the spring. The mean flow rate is 140 cu m per sec. The Colorado is navigable for a distance of 320 km from the mouth.